Inside the Heart: Redefining Transplant Training Through Mixed Reality at RiyalMedical
In the high-stakes world of medicine, few procedures are as intricate and emotionally charged as a heart transplant. Training for such a critical operation demands more than textbooks and traditional simulations—it requires a deep, immersive understanding of human anatomy, surgical precision, and real-time responsiveness. At RiyalMedical, we’ve taken on this challenge by developing a Mixed Reality-based Heart Transplant Experience using WebXR, Unity, and Blender.
This groundbreaking project brings together the best of immersive technology and medical science, enabling students and professionals to engage in a full-scale transplant simulation that’s interactive, web-accessible, and visually stunning. Our platform not only enhances surgical education but also makes it more accessible, repeatable, and safe—a game-changer for medical learning in India and beyond.
Why Heart Transplant in XR??
Heart transplant procedures are complex, time-sensitive, and life-saving. In real life, opportunities to practice such surgeries are extremely limited, especially for students and early-career professionals. At RiyalMedical, we envisioned a solution where aspiring surgeons can learn by doing, without risking a real patient or depending solely on cadaver-based learning.
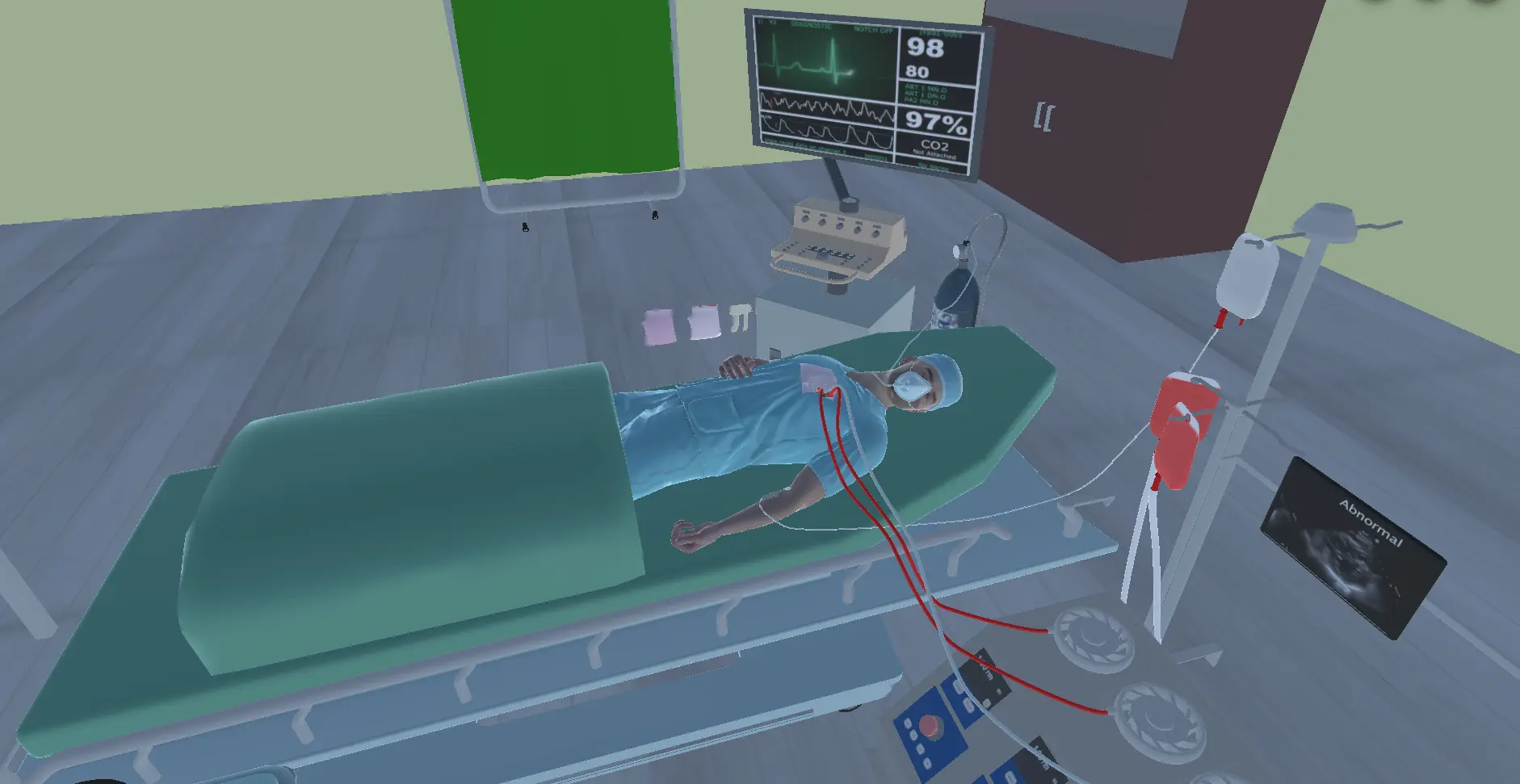
Our WebXR-based simulation is a multi-layered, fully interactive experience where users can walk through the entire transplant process—from donor heart preparation to removal of the failing heart and the final surgical placement. Learners can visualize cardiac anatomy in 3D, interact with surgical tools, and follow step-by-step procedural guidance, all while operating in their actual physical environment.
This approach not only enhances comprehension but also builds muscle memory and decision-making confidence in a safe, controlled environment.
WebXR and Unity: Surgery Meets Accessibility
To ensure the experience is browser-based and device-agnostic, we built the simulation on WebXR, allowing it to run seamlessly across desktops, mobile browsers, and XR headsets—no app installation required. This means that a student in a rural college or a busy hospital can access the entire simulation using nothing more than a browser and an internet connection.
Unity serves as the core engine, enabling high-quality interactivity, real-time rendering, and precise control systems. We integrated medical-grade logic into the simulation, such as heart rhythm checks, organ perfusion visuals, and real-time feedback during critical moments like vascular connection and heart pacing.
To make the experience collaborative and engaging, the simulation also includes optional AI-guided narration and multi-user session capability—allowing educators and students to walk through the transplant process together in a shared virtual environment.
Modeling Life with Blender
Anatomical accuracy was non-negotiable. Using Blender, our design team created detailed 3D models of the human chest cavity, heart, surrounding organs, and surgical instruments. Each element was reviewed by medical professionals and modeled to reflect real-world dimensions, textures, and movement.
The donor and recipient hearts were sculpted with intricate internal and external features—valves, arteries, chambers, and even muscular tissue variations. These weren’t static objects; we animated physiological states such as pre-transplant failure, active circulation, and post-operative integration, making the simulation feel not just educational but alive.
We also optimized every asset to ensure smooth WebXR performance, even on modest devices, without sacrificing visual fidelity.
From Training Tool to Industry Standard
This Heart Transplant Mixed Reality Experience isn’t just a cool simulation—it’s a powerful educational framework built for medical institutions, nursing schools, and health tech academies. RiyalMedical envisions this becoming a licensable module that can be integrated into digital curriculum platforms, smart classrooms, and remote surgical workshops.
- 1. Medical colleges can offer hands-on surgical exposure without resource constraints.
- 2. XR labs can use it to run live workshops or practical exams.
- 3. Hospitals can train residents and interns using repeatable, data-driven simulations.
More importantly, this platform democratizes access to elite surgical training—an especially vital need in emerging economies where cadaver access or high-cost simulators are limited.
